Introduction
Have you noticed that discussions about artificial intelligence replacing human jobs are becoming more frequent? The fear that AI will take over the workforce and leave people unemployed has been around for some time, but the reality is quite different.
Rather than replacing human labor, AI serves as a tool that helps businesses and employees work more efficiently and productively. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) often lack the resources to hire large teams, and virtual assistants and AI-powered tools can ease operations by taking over repetitive tasks and freeing up time for work that requires human creativity and strategic thinking.
Virtual assistants, which have already become an integral part of many businesses, are increasingly leveraging AI tools to perform tasks faster and more effectively. Automated systems assist with content creation, data management, and administrative duties. Rather than replacing them, AI enables virtual assistants to provide better service and manage a higher volume of tasks than would be possible manually.
Statistics show that AI is becoming more integrated into business processes. According to research conducted by the U.S. Chamber of Commerce and Teneo, 98% of small businesses in the United States use some form of AI tool, while 40% utilize generative AI tools such as chatbots and image creation software, nearly double the adoption rate from the previous year. (Source: uschamber.com)
In the United Kingdom, according to the AI Activity in UK Businesses report commissioned by the UK government, 15% of all businesses have adopted at least one AI technology, which equates to approximately 432,000 companies. (Source: assets.publishing.service.gov.uk)
Rather than being a threat, AI serves as an ally that boosts productivity and reduces costs, allowing people to focus on more complex tasks. The best results come from combining human creativity and flexibility with the speed and analytical capabilities of artificial intelligence.
But what exactly separates AI-powered assistants from human virtual assistants, and how do they complement each other? Let’s break it down.
Differences Between AI and Human Virtual Assistants
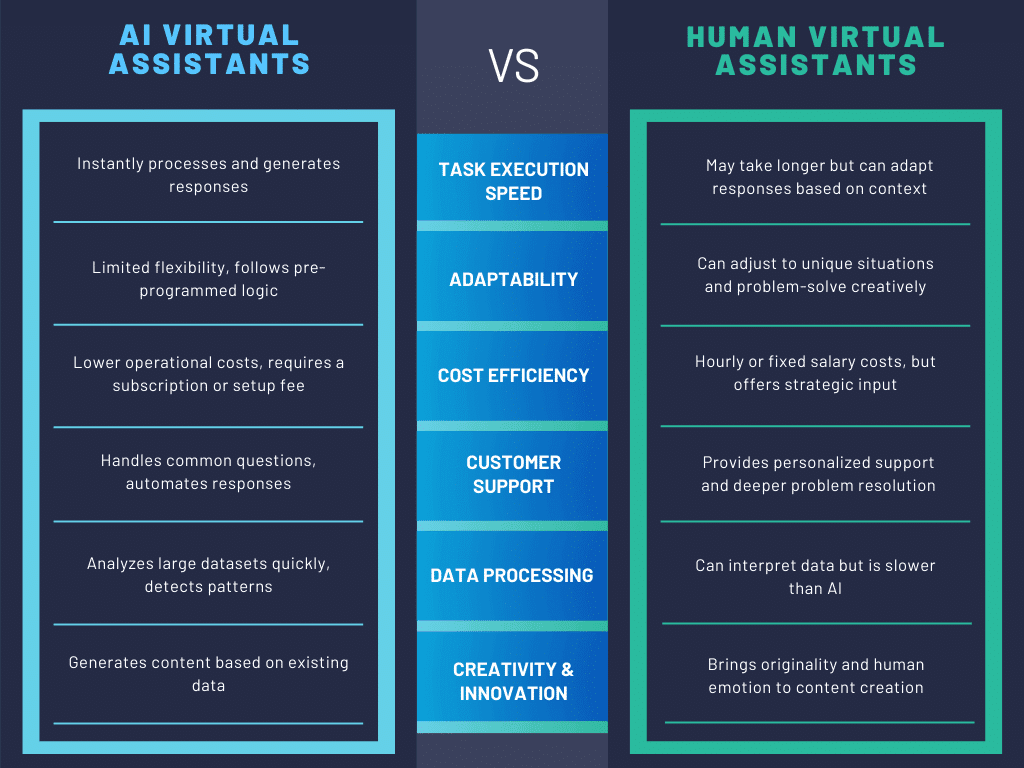
With the increasing adoption of artificial intelligence in business operations, many companies are debating whether they should rely solely on AI-powered assistants, hire human virtual assistants, or find a way to combine both. While AI can automate repetitive tasks and process vast amounts of data, human assistants provide adaptability, critical thinking, and the personal touch that many aspects of business still require.
The key to maximizing efficiency is knowing which tasks are best suited for AI and which require a human approach. Businesses that successfully integrate both often experience higher productivity, better customer satisfaction, and reduced operational costs.
For example, AI-powered assistants can handle data-driven and repetitive tasks at scale, while human virtual assistants excel at building relationships, problem-solving, and handling unique situations that require emotional intelligence.
Let’s take a closer look at the fundamental differences between AI and human virtual assistants and when to use each.
For a deeper look into how virtual assistants operate in different industries, check out The Best Virtual Assistant Service in the USA.
How AI and Human Virtual Assistants Work Together for Maximum Productivity
Many businesses wonder whether they should rely entirely on AI assistants or hire human virtual assistants. The truth is, the best results come when AI and human assistants work together, complementing each other’s strengths.
AI automates repetitive tasks, processes large amounts of data, and speeds up workflows, while human virtual assistants handle personalized communication, creative problem-solving, and strategic decision-making. When integrated properly, this combination allows businesses to reduce costs, improve organization, and enhance customer support.
Where AI and Human Virtual Assistants Work Best Together?
Customer Support
AI chatbots provide instant responses to frequently asked questions, such as order tracking, refunds, and product availability. However, when a customer has a complex issue that requires personalized attention, a human virtual assistant takes over, ensuring a high level of service.
Content Creation
AI-powered tools like Walter Writes can generate blog post drafts, email templates, and social media content. However, human virtual assistants refine, edit, and personalize the content to align with the brand’s style and tone.
Data Management and Insights
AI analyzes customer behavior, identifies patterns, and provides detailed reports. Human virtual assistants use this information to develop marketing strategies, improve customer engagement, and personalize outreach efforts.
Scheduling and Task Management
AI handles basic scheduling tasks, such as setting appointments and sending reminders. However, human assistants step in to prioritize tasks, reschedule as needed, and ensure important deadlines are met.
Lead Generation and Outreach
AI tools gather potential leads and generate suggested outreach messages. Virtual assistants add a personal touch, adjusting communication based on client preferences and responses.
A Real Example: AI and Human Virtual Assistants in Action
A growing e-commerce business is struggling to keep up with customer inquiries. With an increasing number of orders, they receive hundreds of messages daily asking about order status, return policies, and product availability. The business decides to implement a hybrid approach, combining an AI chatbot with human virtual assistants.
AI chatbot handles routine inquiries instantly – When a customer asks, “Where is my order?” or “What is your return policy?”, the AI chatbot provides an immediate and accurate response. This reduces wait times and ensures that customers get quick answers, even outside of business hours.
Escalation to a human virtual assistant for complex requests – If a customer has a billing dispute, special request, or product issue, the chatbot recognizes that human intervention is needed. It transfers the conversation to a virtual assistant who can understand context, provide a personalized response, and resolve the issue efficiently.
AI analyzes customer behavior and purchasing patterns – The chatbot collects data on frequent customer inquiries and shopping trends, allowing human virtual assistants to adjust marketing campaigns, improve product recommendations, and create targeted promotions. If a certain product receives many questions about sizing, the assistant updates the website with clearer descriptions.
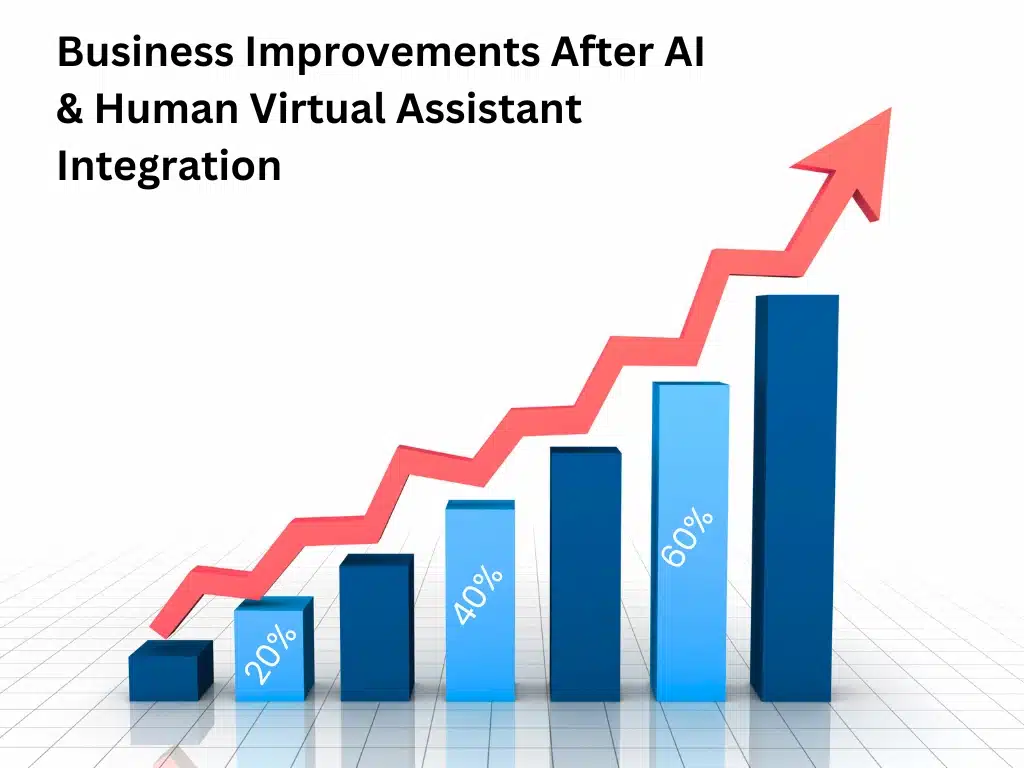
After a few months, the business sees noticeable improvements:
✅ Response times drop by 60%, leading to higher customer satisfaction.
✅ Human assistants are more productive, handling fewer repetitive questions and focusing on high-value interactions.
✅ Sales increase by 20% because of better personalized marketing strategies informed by AI insights.
This balanced approach ensures that AI automation improves response times, while human virtual assistants maintain the personal touch needed for customer loyalty. Businesses that apply this model can scale their operations smoothly without sacrificing service quality.
How to Successfully Implement AI and Human Virtual Assistants in Your Business
Integrating AI tools and human virtual assistants into a business requires clear planning and a structured approach. Businesses that find the right way to combine both often see better productivity, lower costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
This section outlines practical steps to help businesses set up a system where AI and human assistants work together effectively.
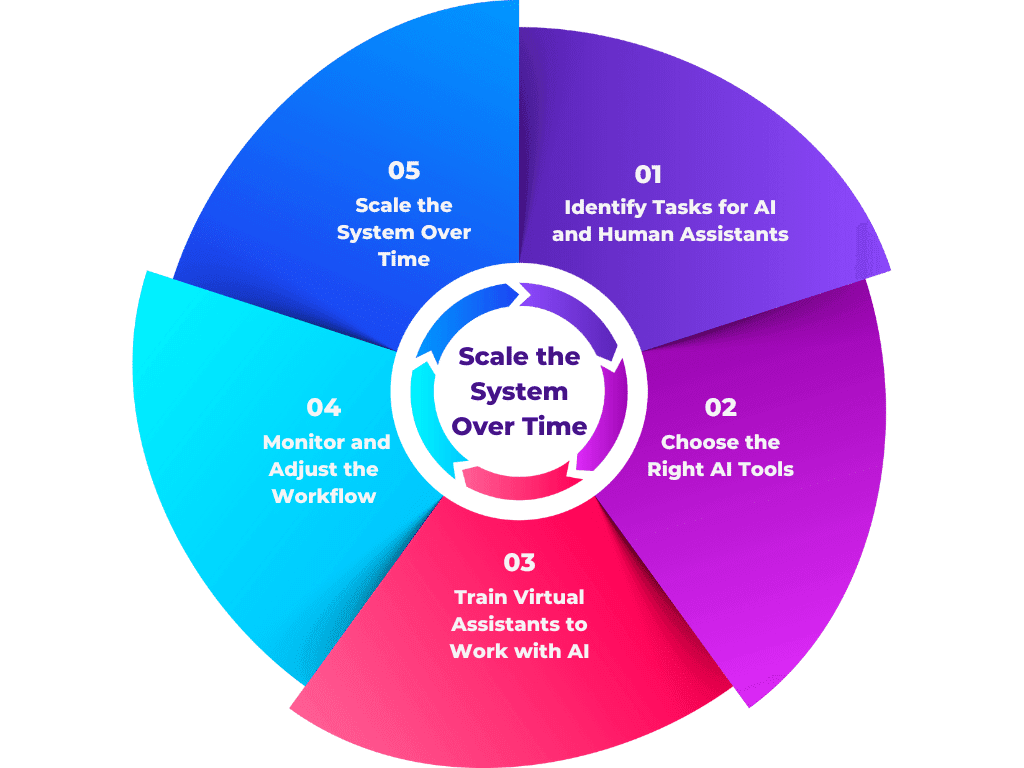
1. Identify Tasks for AI and Human Assistants – Before making any changes, it’s important to list all the tasks that need to be managed.
- AI is best suited for repetitive and data-heavy tasks like scheduling, handling frequently asked customer questions, and generating reports.
- Human assistants should focus on tasks that require judgment, personal interaction, and creative thinking, such as resolving complex customer issues and adjusting marketing strategies.
A structured task list will help decide which areas can be automated and which need direct human input.
2. Choose the Right AI Tools – There are many AI tools available, but choosing the right one depends on business needs.
- For content automation: Walter Writes helps businesses create drafts for emails, blog posts, and ads, which human assistants can refine.
- For customer service: AI chatbots handle simple inquiries, while human assistants step in for detailed responses.
- For data analysis: AI systems track customer behavior, while human assistants use that data to improve services and sales strategies.
Testing different tools on smaller tasks first can help decide which options provide the best results.
3. Train Virtual Assistants to Work with AI – For AI and human assistants to work well together, training is needed.
- Virtual assistants should understand how AI tools function so they can use them efficiently.
- AI-generated content should be checked and edited when necessary to match company standards.
- Teams should have clear guidelines on when a task should be handled by AI and when human input is needed.
Providing short training sessions will make the transition smoother.
4. Monitor and Adjust the Workflow – Once AI and human assistants are working together, performance should be reviewed regularly.
- Are response times improving?
- Is AI helping assistants complete tasks more quickly?
- Do customers prefer AI responses, or do they seek human interaction more often?
Tracking results and making adjustments helps refine the process over time.
5. Scale the System Over Time – After testing on a smaller scale, AI can gradually be used for more complex tasks.
- If AI chatbots perform well with basic customer service, they can handle additional tasks like managing orders and returns.
- If AI-generated content is helping with marketing, businesses can expand it to more platforms.
- As teams gain experience with AI, they can adjust the balance between automation and human involvement.
Businesses that gradually expand their AI and human assistant collaboration often see the best results.
Challenges and Solutions in Using AI and Human Virtual Assistants
While combining AI and human virtual assistants offers numerous benefits, businesses often face obstacles when trying to implement both successfully. AI can process large amounts of data, automate repetitive tasks, and provide instant responses, but it has limitations when dealing with context, emotions, and problem-solving.
On the other hand, human assistants bring creativity, adaptability, and interpersonal skills, but they have time constraints and require compensation. The key to successful integration is recognizing potential challenges and applying effective solutions that ensure AI and human assistants complement each other.
This section outlines the most common issues businesses face when using AI and human assistants together – and how to solve them.
Challenge 1 – AI Limitations in Handling Complex Requests
Issue: AI chatbots and automation tools can efficiently handle structured, predictable interactions. They respond quickly to frequently asked questions, appointment scheduling, and order tracking, but they often fail when context or emotion is required. AI lacks the ability to read between the lines and fully grasp the nuances of human communication.
For example, if a customer is frustrated about a delayed order and uses sarcastic language, an AI chatbot might not detect the tone correctly. Instead of de-escalating the situation, it could respond robotically or with irrelevant information, frustrating the customer further.
Solution: Businesses should create hybrid systems where AI handles routine requests, while human assistants manage complex or emotionally sensitive situations. A smart routing system should be in place so that AI escalates issues to a human assistant when necessary.
Example:
- AI chatbot answers a basic shipping inquiry.
- If the customer expresses dissatisfaction, AI detects keywords like “angry,” “problem,” or “refund” and immediately connects them to a human assistant.
- The human assistant takes over and resolves the issue with empathy and problem – solving skills.
By setting up clear escalation pathways, businesses can prevent frustration while still benefiting from automation.
Challenge 2 – Resistance to AI Adoption
Issue: Many employees and customers are hesitant to embrace AI due to concerns about job security, trust, and service quality. Employees may fear that AI will replace their roles, while customers may worry that AI interactions lack personalization.
According to a Pew Research Center study from February 2025, 52% of American workers express concern about the future impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on jobs, while 36% feel hopeful about it. (Source: uschamber.com)
Solution: To overcome skepticism, businesses should:
- Position AI as a support tool, not a replacement. Show employees how AI helps them focus on more meaningful work by automating time-consuming tasks.
- Educate teams on AI capabilities and limitations, providing training on how to collaborate with AI tools.
- Be transparent with customers, ensuring that human support is always available when needed.
Example: A company implementing an AI-powered chatbot for customer service can include a message at the start of each conversation, such as: “I’m an AI assistant here to help! If you need to speak with a human, just type ‘agent’ at any time.”
This reassures customers that AI is there to assist, not replace human support.

Challenge 3 – Ensuring a Smooth AI-Human Collaboration
Issue: If AI and human assistants are not well-integrated, workflows can become disorganized, leading to delays, miscommunication, and inefficiencies. If a chatbot mishandles an inquiry before transferring it to a human, the assistant might lack the full context, frustrating both employees and customers.
Solution:
- Clearly define AI and human responsibilities. Create standard operating procedures (SOPs) that outline when AI should handle a task and when human involvement is required.
- Train virtual assistants to work with AI tools rather than against them. For example, they should know how to review AI-generated responses, correct errors, and make adjustments when needed.
- Use a shared system where human assistants can see AI interaction history before taking over. This prevents asking customers to repeat themselves, which is a common complaint in AI-human hybrid models.
Example:
- A CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system can store chat histories.
- When an AI chatbot escalates a case, the human assistant can see the entire conversation before responding, ensuring a smoother transition.
Businesses that implement a well-structured AI-human workflow experience fewer dropped conversations and higher customer satisfaction.
Challenge 4 – Accuracy and AI-Generated Mistakes
Issue: AI tools are trained on large datasets, but they can still misinterpret queries, generate inaccurate information, or apply outdated responses. AI-generated content, while fast, sometimes lacks nuance, originality, or proper fact-checking.
Example: A business using AI for content marketing may find that the AI writes grammatically correct but repetitive blog posts. The AI might also generate misleading product descriptions if it misinterprets data.
Solution:
- Always have human review processes in place. AI-generated content and responses should be checked and refined before being published or sent to customers.
- Train AI models with real-time data to prevent outdated responses. Businesses should regularly update AI tools to ensure accuracy.
- Use AI tools for drafting and ideation, not final output.
Example:
- AI generates a blog draft → Human assistant refines it, ensuring clarity and originality.
- AI provides a product recommendation → Human assistant personalizes the suggestion based on customer preferences.
A combination of AI-generated efficiency and human refinement leads to high-quality, reliable communication.
Challenge 5 – Security and Data Privacy Concerns
Issue: AI tools process large amounts of customer data, making data security a priority. If security protocols are weak, businesses risk data breaches, compliance violations, and customer distrust.
Example: A chatbot collecting customer addresses and payment details must comply with regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) or CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act). Failure to protect this data can result in legal consequences and reputational damage.
Solution:
- Choose AI tools with strong security features, such as encryption and two-factor authentication.
- Limit AI access to sensitive data and ensure that only authorized personnel can view it.
- Comply with legal data protection frameworks by anonymizing personal information when possible.
Example: A bank using AI for customer support might:
- Restrict AI from storing full credit card numbers.
- Use human verification for transactions beyond a certain amount.
By taking a proactive approach to AI security, businesses can build trust with customers while maintaining compliance with global regulations.
Combining AI with human virtual assistants can provide faster workflows, better customer engagement, and lower operational costs. However, potential challenges must be addressed early to ensure that AI remains a tool for supporting and enhancing human capabilities, rather than replacing them.
By applying structured workflows, proper training, and clear security protocols, businesses can successfully integrate AI while maintaining accuracy, trust, and a personal touch.
The Future of AI and Human Virtual Assistants in Business
AI and human virtual assistants are evolving, reshaping how businesses operate. AI is becoming more refined, capable of handling larger datasets and generating responses that feel more natural. At the same time, human assistants are shifting toward roles that require critical thinking, creativity, and personal engagement.
As AI tools improve, they will take over more repetitive and data-driven tasks. Businesses are already seeing AI-powered chatbots provide instant responses, AI-driven analytics predict customer behavior, and AI writing assistants generate content drafts. However, there remains a strong need for human oversight. The ability to interpret context, build relationships, and make strategic decisions still rests with people.
Rather than replacing human assistants, AI is shaping a new way of working. Virtual assistants are learning to collaborate with AI, using it to streamline their tasks while maintaining a personalized approach to customer interactions. Companies that embrace this balance between automation and human adaptability will likely achieve the best results.
Looking ahead, businesses that integrate AI effectively will gain a competitive advantage. AI will continue to develop, but human insight will remain invaluable in shaping business strategy, ensuring quality control, and providing a human touch where automation falls short. The future is not about choosing between AI and human assistants – it’s about using both in a way that maximizes productivity and creates better experiences.
Conclusion
AI and human virtual assistants work best when used together. AI speeds up repetitive tasks, processes large amounts of data, and helps businesses handle customer interactions at scale. Human assistants focus on communication, creative tasks, and problem-solving where technology falls short.
Businesses that balance these two approaches see better results. While AI brings automation, human judgment is still needed for complex situations. The key is to set up clear roles, provide training, and regularly check performance to make sure AI and human assistants complement each other.
Looking ahead, AI will continue to improve, but people will remain at the center of decision-making and customer relationships. The companies that combine these strengths will stand out, providing faster service without losing the personal touch that builds trust.


